What is Cloud Computing?
Over 20% of organizations say they have little to no idea how much different aspects of their business cost as it relates to the cloud – (CloudZero, The State of Cloud Cost in 2024)
Cloud computing has changed how we work and function in business over the last decade. It offers unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. In simple words, it refers to providing computing services over the Internet by large remote servers, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and more. This way, access to such resources is available on-demand without the necessity of physical infrastructure.
Cloud computing also plays an essential role in our daily lives. Whether it’s playing a video game hosted in the cloud, streaming a movie on Netflix, or using a cloud service like Google Gmail,
When it comes to applicability, scalability, and flexibility, the cloud computing architecture outperforms traditional on-premises infrastructure by a greater margin.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing benefits businesses in many ways. Companies looking for affordable ways to replace the legacy system, can not miss this section, presenting the top benefits to encourage them to get the cloud.
Globally, the cloud computing market will surpass $1 trillion by 2028. (Precedence Research)
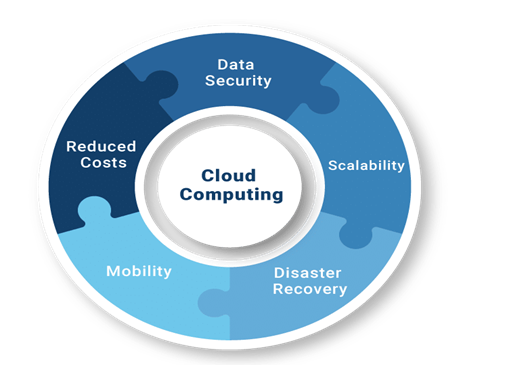
- Scalability
There are many benefits cloud computing offers. Scalability is one of the most distinctive. This is indeed the easiest thing for businesses to do after adjusting to the initial changes. They can change their resources as per needs and watch out for over-supply and under-utilization of hardware.
- Disaster recovery
Sometimes incidents like natural disasters or operational inefficiencies are inevitable. In modern times with a great amount of data being generated every second, no company can afford incidents, that can harm their data and sources. Cloud computing offers services to store data in the cloud, and ensure all your data is immune to such incidents. Even if anything or everything is lost, data recovery functions will always have the backup to save your day in emergencies.
- Enhanced collaboration among teams
Clear communication and establishing an appropriate co-working environment is essential for people to work in a team. Cloud computing does what is needed to encourage collaboration among employees. Teams can communicate access and share files in real-time from anywhere in the world. With cloud computing teams can work in a more collaborative and comfortable environment of getting the work done.
- Cost Savings
Traditional systems often build up on exponentially expensive servers and hardware and not every company can afford them. Although costs are another major incentive for going cloud, they minimize the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure and maintenance, which allows companies to have more convenient ways to scale their business while being cloudsured.
- Data security
Data security concerns have always been a headache for companies seeking affordable ways and bid adieu to the traditional ways of storing and sharing data. To address the most pressing issues with data storage Cloud providers typically invest heavily in robust measures for security, making it much easier for companies to safeguard sensitive data.
Applications of Cloud Computing
As data generation is at an all-time high, growing consumer demands and their easy-to-online services, make it difficult for companies to run their business with in-house computing servers. Therefore, it becomes critical that companies leverage diverse ways and reach all aspects of modern life.
The global computing market is projected to reach a market value of $923 billion at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15% by the end of 2027, compared to the $368 billion valuation in 2021. (Knowledgehut)
The flexibility of cloud computing applies to many different sectors. Let’s dive into a few of the most popular uses.
- Data Storage and Backup
Cloud-based storage solutions like Google Drive or Dropbox have changed the ways of storing and backing up data. A user will be able to retrieve files by accessing any device connected to an internet connection. The availability of data between the users further helps in collaboration without much hassle. Additionally, automatic backup features prevent important data from getting lost, hence making them an incredibly important tool for both individuals and companies.
- Business Uses
Cloud-based business applications range from project management tools to communication platforms, therefore offering efficiency and productivity. So, the tools that allow real-time collaboration are Slack and Asana, while the management of financials is streamlined through software such as QuickBooks Online.
- Customer Relationship Management
The cloud-based CRM systems include Salesforce, empowering organizations to manage interactions with customers much more effectively. Indeed, it provides insights into customer behavior, thereby enabling businesses to tailor their marketing strategy and improve customer satisfaction.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP systems, for example, SAP S/4HANA, will play a prime role in integrating many business processes. They will enable organizations to operate more cohesively and efficiently by centralizing finance, human resources, and supply chain management-related data.
- Big Data Analytics
Cloud computing allows the storing and processing of heavy data volumes to work out actionable information in business organizations. It gives them the right analytics software tools from such cloud-based platforms as AWS from Amazon and Microsoft Azure, helping determine the decisions taken based on this data.
- Software Development and Testing
The Cloud changed software development completely, allowing developers to create scalable environments for testing and deployment. Heroku and GitHub Actions streamline this process to make fast-paced development cycles possible together with continuous integration.
- E-commerce
The uprise of e-commerce is of course cloud computing that is significantly supported. Cloud infrastructure makes it easy to set up an online store using platforms such as Shopify and WooCommerce for platforms that store payment processing, inventory management, and storage of customer data.
- Internet of Things (IoT)
Cloud computing is at the back of IoT, interlinking millions of devices and allowing them to communicate. Most of the smart home systems, industrial IoT applications, and health monitoring devices rely on processing and data analysis that they produce in large amounts through cloud services.
- Entertainment and Media Streaming
Innovations like Netflix and Spotify have reshaped the face of entertainment consumption. They deliver high-quality streams to millions of customers across the world by leveraging the scalability of cloud infrastructure, which can scale up to a point of maximum usage during a particular period.
- Healthcare and Telemedicine
Cloud computing supports telemedicine solutions, which enable remote consultation and patient monitoring in healthcare. In addition, cloud-based EHR systems enhance the quality of patient care by providing immediate availability of information to healthcare professionals.
- Education and E-learning
The sector of education has gone for cloud technology, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. Online learning platforms like Coursera and Zoom use cloud computing for the transmission and delivery of educational content while enhancing remote learning through these platforms, thus making education more accessible than ever.
- Financial Services and Banking
Cloud computing has penetrated all the minutest corners of the financial services industry. Banks and fintech companies make use of cloud-based solutions to manage data, detect fraud, and meet regulatory requirements. Thus, this approach ensures more security along with lower operational costs.
- Cloud Computing in Different Markets
Apart from basic consumer use, cloud computing has a great influence in large sectors that cater to different businesses. These large-scale industries are also among the heavy users of cloud computing to meet the demands of large data sets of consumers of different demands. Here are the following industries benefiting from cloud computing.
- Manufacturing Industry
Cloud computing in manufacturing uses the concept of managing production with the application of real analytics and supply chain management. Cloud-based solutions help in inventory management, logistics, and improved operational efficiency for all manufacturing plants.
- Retail Industry
Retailers use cloud computing to manage stock, analyze customer behavior, and tailor marketing campaigns. Businesses can therefore adapt their products to better customer experiences through patterns in purchasing behavior.
- Government and Public Sector
Cloud solutions are also increasingly being adopted by governments to enhance service delivery and citizen engagement. Cloud computing enables the promotion of better management of data and coordination among the departments for more efficient public services.
- Transport and Logistics
Such cloud-based platforms are, therefore, crucial in the transportation and logistics area, offering real-time tracking and data analysis. Companies can optimize routes, monitor fleets, and increase supply chain transparency, resulting in cost reductions and improved customer service.
In Conclusion: Challenges and Considerations
Real-world applications of cloud computing are so vast and massive that they will transform the way we live and work in the coming years. As more and more organizations come to realize the benefits of cloud technology, the role of cloud computing for efficiency, innovation, and collaboration will continue to expand.
Businesses may navigate the challenges associated with cloud computing, and with their full potential, open up opportunities for a more connected and efficient global workforce.
However, cloud computing also poses challenges. Its security is also a concern. Organizations need to be assured that data is not tampered with. It is because regulation in the form of GDPR can be elaborate within a cloud, so organizations get wary. The business needs to especially consider vendor lock-in, and it is not so easy or cheap to shift data between different cloud services.
Lastly, Get cloud-assured ASAP.
Also Read:
Full Stack Development for Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
Cloud Complexities and Possible Solutions!
Building Data Pipelines for Multi-Cloud Environments: Challenges and Solutions



Add comment