Scrum, a framework within Agile project management, emphasizes efficiency, transparency, and iterative progress. To facilitate this, Scrum defines roles, events, and artifacts that guide teams toward building and delivering value incrementally.
Among these, Scrum artifacts serve as crucial information radiators, providing visibility and alignment within teams. These artifacts help teams track work progress, prioritize tasks, and ensure transparency, keeping everyone aligned and focused on the shared goals.
This blog will provide an insightful overview of Scrum artifacts, covering the three main types—the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Product Increment—and offering insights into best practices, common challenges, and popular tools for managing them effectively.
The Three Main Scrum Artifacts
Scrum defines how many roles, events, and artifacts are needed for effective team alignment and project success. The three main Scrum artifacts are:
- Product Backlog,
- Sprint Backlog, and
- Product Increment
Each has unique purposes but collectively aim to foster transparency, inspection, and adaptability. Let’s explore each in detail.
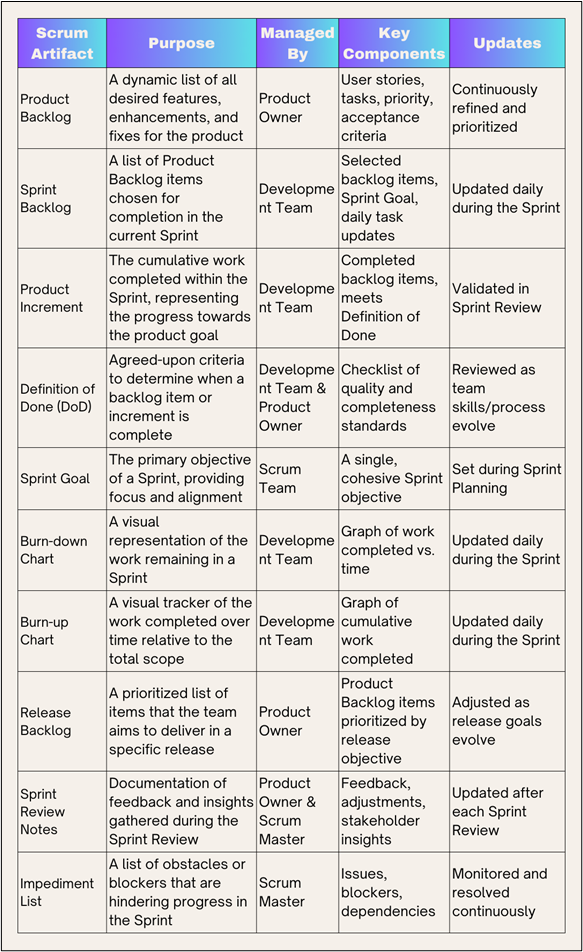
Product Backlog
The Product Backlog represents a comprehensive list of all the tasks, features, enhancements, and fixes required to complete a product. As the single source of requirements for any changes, the Product Backlog represents the scope of work that will evolve throughout the project. This artifact is dynamic, adapting to changes in the market or stakeholder requirements, making it central to agile artifacts in Scrum.
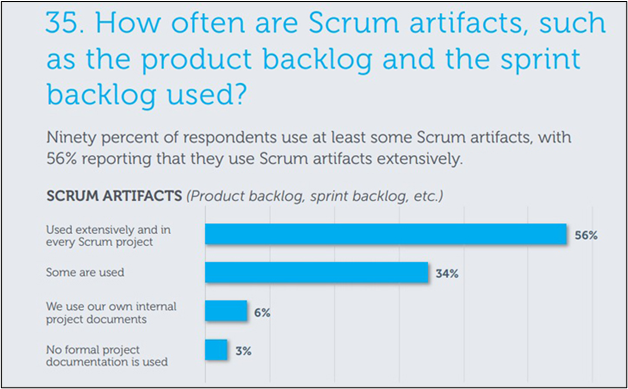
Understanding the Product Backlog
It’s managed by the Product Owner. The Product Backlog is constantly refined and adjusted as new requirements or priorities emerge. This artifact provides the team with a transparent view of what’s coming up, helping to ensure that development aligns with business goals.
Components of a Product Backlog
A well-organized Product Backlog contains various items or “user stories,” each describing the desired functionality. Each item has a description, priority level, and estimated effort, which aids in planning and sprint prioritization. It also contains acceptance criteria, outlining conditions under which a backlog item will be considered complete.
Product Backlog Refinement
The Product Backlog Refinement process is a continuous process of defining and modifying items in the product sourcing backlog by the Product Owner and the team. During this procedure, larger items are decomposed into smaller ones, and their volume and position on the lists are also revised.
Role of the Product Owner
The person responsible for the management of the Product Backlog is the Product Owner. The biggest charge on the specified person has the aim of being sure that the product repository contains business virtues. They manage the expectations of multiple stakeholders, select important items, work alongside the development group to resolve outstanding issues if need be.
Sprint Backlog
Once the Product Backlog is refined, the Sprint Backlog comes into play. The Sprint Backlog consists of selected items from the Product Backlog that the development team locks in to complete within a specific Sprint or iteration. This artifact is designed to focus the team on immediate, actionable goals.
Creating a Sprint Backlog
The Sprint Backlog is created during Sprint Planning, where the team selects tasks from the Product Backlog based on the
- Sprint Goal,
- capacity, and
- past performance.
By planning realistic objectives, teams ensure they’re equipped to deliver quality outcomes within the Sprint duration.
Sprint Goal
The Sprint Goal is a short, guiding objective that aligns the selected backlog items with a unified purpose. It acts as a motivating factor, helping the team focus on a single deliverable and facilitating decision-making during the Sprint.
Daily Updates to the Sprint Backlog
To ensure transparency, the Sprint Backlog is updated daily during the Daily Scrum. This helps track progress and address any blockers, allowing the team to adapt and refocus as needed. Frequent updates ensure that the Sprint Backlog remains relevant and aligned with the Sprint Goal.
Product Increment
The Product Increment represents the cumulative work completed during a Sprint and serves as the team’s contribution to the overall product. This artifact ensures that every Sprint results in a potentially releasable version of the product, showcasing incremental progress.
Definition of Done
Each Product Increment must meet a clear Definition of Done (DoD). It is a set of criteria that must be fulfilled for an increment to be considered complete. The DoD fosters quality by setting standards that every Increment must meet, ensuring that each new Increment is ready for potential release.
Incremental Value Delivery
A key aspect of Agile and Scrum artifacts is that the increment enables teams to deliver value to stakeholders regularly, allowing for feedback and adjustments. This incremental delivery helps ensure that the product keeps developing in alignment with user needs and market trends.
Sprint Review and the Product Increment
To get feedback on the Product Increment, a Sprint Review presentation is made to stakeholders. This process of inspection ensures that the Increment fits within the business context and that improvements can also be made before the next Sprint begins.
Best Practices for Managing Scrum Artifacts
Effectively managing Scrum artifacts requires discipline, collaboration, and transparency. Here are some key practices to consider:
Transparency and Visibility
Maintaining transparency in each Scrum artifact promotes trust and helps everyone stay aligned on progress. Regularly reviewing and updating artifacts ensures they reflect the most current information and provide clarity to all stakeholders.
Regular Updates and Maintenance
Frequent refinement of the Product and Sprint Backlogs is essential. Product Backlog Refinement sessions should occur regularly to keep items well-defined, estimated, and prioritized.
Collaboration Among Team Members
Scrum artifacts work best when there’s strong collaboration among team members. Involving the entire team in Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, and Sprint Review meetings fosters a shared understanding and accountability.
Common Challenges with Scrum Artifacts
While Scrum artifacts facilitate effective project management, challenges can still arise.
Overcomplicating Artifacts
It’s common for teams to add too many details or unnecessary documentation, which can make artifacts unwieldy. The focus should remain on simplicity and clarity, ensuring that artifacts serve their purpose without adding excessive overhead.
Neglecting Regular Updates
Failure to track the Product and Sprint Backlogs results in old priorities which do not reflect the goals of the business. These documents need to be updated regularly so that they correspond to the currently accepted aims of the project.
Misalignment Between Artifacts and Team Goals
When the Scrum artifacts do not conform with the expectations of the team, it creates a level of ambiguity and demotivation. However, different artifacts with specific aim help focus the effort of all participants towards the same goal.
Tools for Managing Scrum Artifacts
Managing Scrum artifacts manually can be challenging, especially for larger teams. Here are some popular Scrum software solutions that simplify artifact management:
Popular Scrum Software Solutions
- Jira by Atlassian – A versatile tool that allows teams to track backlog items, set up Sprint goals, and monitor progress on a detailed level.
- Trello – A visual project management tool (PMT), Trello is especially useful for smaller teams looking to manage Product and Sprint Backlogs easily.
- Scrumwise – Focused on Scrum teams, Scrumwise offers an intuitive way to track artifacts and team progress.
- Azure DevOps – Integrates Scrum artifacts with development tools, making it easier for technical teams to manage backlogs and increments.
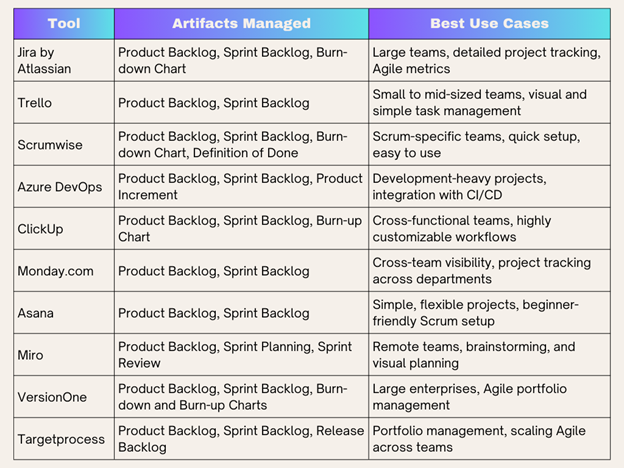
Integrating Artifacts with Project Management Tools
When integrating Scrum artifacts into broader project management tools, consider tools like Asana or Monday.com, which provide cross-functional visibility. Using the right tool for your team can make it easier to collaborate, communicate, and keep track of Scrum activities.
Conclusion: Maximizing the Value of Scrum Artifacts
Scrum artifacts promote transparency, alignment, and evolution of the Agile teams which is something that needs to be encouraged at all times.
When the Product Backlog, the Sprint Backlog, and the Product Increment are properly managed, the teams are oriented to the direction of delivering value incrementally, improving the product predictably, and satisfying user needs in an efficient manner.
Watching out on the best practices to observe, the right tools to use, and the level of transparency to maintain are issues that do assist in attaining the objectives of a scrum team amidst challenges.
In the end, in order to encourage continuous evolution Scrum describes roles, events and artifacts. When the efficiency of those artifacts is properly used, the teams will be able to enhance their efficiency and produce the desirable results, all which are in line with the Agile philosophy of flexibility, openness, and customer fulfillment.


Add comment